Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Moriyama, Hirotake*
JNC TJ8400 2000-050, 47 Pages, 2000/03
In support of the safety assessment of geologic disposal of high levcl radioactive wastes, the solubility of transuranium elements was studied. The solubility of PuO
 xH
xH O was measured undcr a reducing condition, and the solubility product K
O was measured undcr a reducing condition, and the solubility product K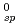 and the stability constant
and the stability constant 
 of Pu(OH)
of Pu(OH) were obtained. The obtained K
were obtained. The obtained K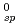 value was found to be much smaller than that predicted by Rai et al. from its dependence on ionic radius. Also, the solubility of PuO
value was found to be much smaller than that predicted by Rai et al. from its dependence on ionic radius. Also, the solubility of PuO 3
3  xH
xH O was measured under an oxidizing condition and the solubility product K
O was measured under an oxidizing condition and the solubility product K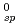 was obtained. In the analysis of hydrolysis constants of actinide ions, it was found that the systematic trend of the hydrolysis constants was well explained by the hard sphere model considering the effective charges of actinide ions.
was obtained. In the analysis of hydrolysis constants of actinide ions, it was found that the systematic trend of the hydrolysis constants was well explained by the hard sphere model considering the effective charges of actinide ions.
Oka, Yoshiaki*; Koshizuka, Seiichi*
PNC TY9602 97-005, 66 Pages, 1997/03
no abstracts in English
Fukuda, Takanari; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
no journal, ,
The presenters have developed a new fluid-rigid coupled particle method for the estimation of the relocation of in-core structures mechanically interacting with fluid phases existing in a reactor. Amid a severe accident, there might exist relatively large in-core structure, the scale of which is comparable to that of the maximum spatial scale of the fluid (e.g. scale of containment vessel). Such a calculation configuration can result in numerical instability with the conventional fluid-rigid weakly coupled methods. Hence, we have derived fluid-rigid strongly coupled time-development equations on the basis of Hamilton's least action principle and developed a new particle method for solving those equations numerically.